Uterine Cancer
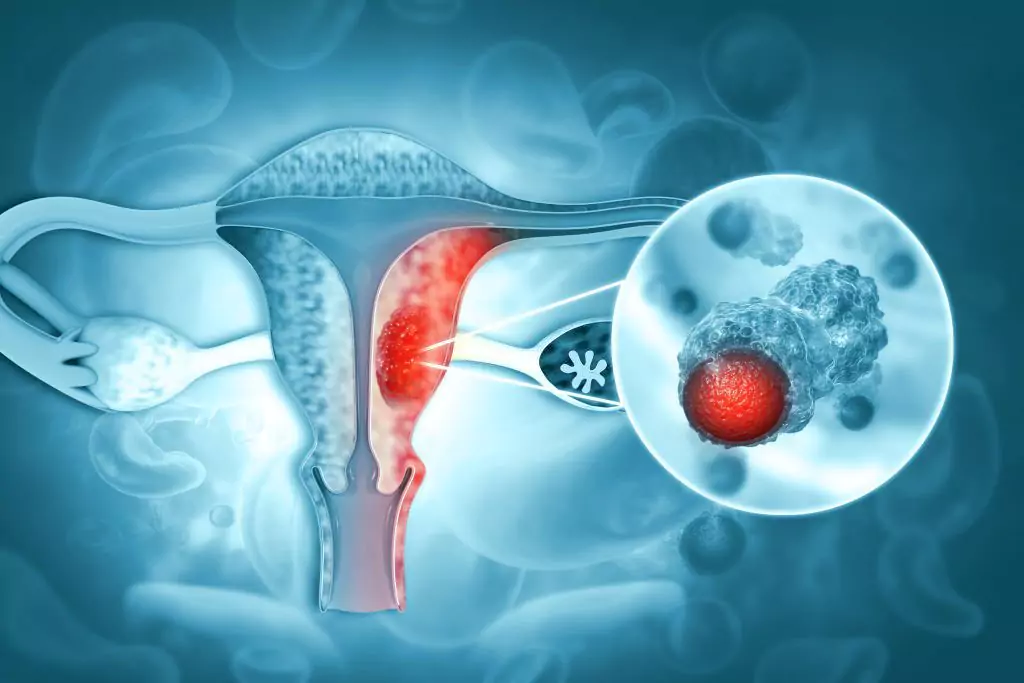
Endometrial cancer is a cancer of the uterus. It is one of the commonest gynecologic cancers seen in women worldwide. It is usually seen in the elderly, between the ages of 60-70. Women who carry high-risk disease-causing mutations can develop this cancer in their 40s and 50s.
What is Endometrial Cancer?
Endometrial cancer is a cancer of the uterus. It is one of the commonest gynaecologic cancers seen worldwide. It is usually seen in the elderly, between the ages of 60-70. Women who carry high-risk disease-causing mutations can develop this cancer in their 40s and 50s.
There are 2 types of uterine cancers seen, they are classified based on the differences in their histopathology.
Type 1 Tumours
These are usually low grade, slowly growing cancers, seen in 80% of women diagnosed with uterine cancer. Endometrioid histology is the commonest type seen in the majority of the tumours.
They occur due to excessive hormonal stimulation (due to estrogen), they carry a good prognosis and may be preceded by a condition called atypical or complex endometrial hyperplasia, which is a pre-cancerous condition.
Type 2 Tumours
These account for the remaining 20% of uterine cancers. These are aggressive cancers, usually high grade and are fast spreading. Histology types seen are endometrioid, clear cell, mucinous, serous, undifferentiated. They carry a high risk of recurrence and an intermediate to poor prognosis. They are not caused by hormonal stimulation.
Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma of Uterus is the type of cancer usually diagnosed in the majority of women.
Besides the above types, uterine cancers can also be classified based on the unique molecular characteristics that define each cancer.
Uterine
Sarcomas
These are a rare type of uterine cancers, occurring in less then 10% patients. These cancers are extremely aggressive, fast spreading, usually diagnosed in the advanced stages and carrying a high risk of recurrence. They are usually seen post 60 but can occur in younger women at times.
Uterine sarcomas can be low grade or high grade.
Leiomyosarcoma is the commonest uterine sarcoma seen. Other types are Undifferentiated sarcoma, Carcinosarcoma & Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma which may be low or high grade.
Signs and symptoms of uterine sarcomas
- Unusual vaginal bleeding or discharge
- Lower abdominal pain or heaviness in pelvic area
- Loss of appetite
- Postmenopausal spotting or bleeding
- Protruding mass through the vagina in advanced cases
- Fatigue or weakness
- Can often be mistaken for a uterine fibroid (leiomyoma).
Risk Factors
For uterine sarcomas include pelvic radiation, long term use of tamoxifen for over 5 years and genetic conditions like childhood retinoblastoma,
Diagnosis
May be suspected on an ultrasound performed for the above symptoms. A disproportionately large uterus may be seen due to the cancer.
Endometrial biopsy or a biopsy of the uterine mass verifies the diagnosis.
Treatment
A radical surgery is required with removal of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes & lymph node dissection.
Depending on the grade and type of sarcoma, and the stage of the disease, chemotherapy and radiation are usually required.
Stage 4 uterine sarcomas cannot be cured, they are inoperable and require chemotherapy & targeted therapy for disease control.
Early signs of Uterine Cancer
- Uterine cancer often shows no symptoms in its early stages.
- Abnormal bleeding is the most common symptom, seen in 75-90% of cases, and can occur in premenopausal and postmenopausal women.
- Any type of bleeding besides the normal menstrual cycle should be investigated.
- Incidental detection through a routine sonography or PAP smear (abnormal endometrial cells may be detected during a PAP smear done for cervical cancer screening)can also lead to a diagnosis.
- As the cancer progresses, symptoms such as lower abdominal pain, urinary complaints, and weight loss may develop.
- Repeated episodes of per vaginal bleeding can cause severe weakness and anaemia.
- Spread to the lungs can cause coughing, chest pain, and breathlessness.
- Advanced stages may show spread to lymph nodes and liver.
- It’s important to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment if any abnormal symptoms are present.
- Early detection and treatment increase chances of survival.

Our Survival Stories
Son of a patient with stage 4 uterine cancer that spread into the lungs.
If you see any concerning signs or symptoms,
schedule an appointment with the doctor now.
Uterine Cancer Symptoms
What are the symptoms of Uterine Cancer?
Bleeding
Postmenopausal spotting or bleeding
Recurrent Genital Pain
Pelvic heaviness or pain ,or lower abdominal pain
Dysuria
Constipation or difficulty urinating

Anorexia
Loss of appetite or weight loss
Fatigue
A feeling of tiredness and weakness
Swelling
Swelling or bloating in the lower abdomen or pelvis
10 Risk factors for Uterine Cancer


Old Age
Older age is a primary risk factor for uterine cancer.

Long term exposure to unopposed oestrogen stimulation
Can result in the eventual development of uterine cancer. This can occur due to oestrogen intake in the form of tablets, skin patches or vaginal rings, when it is used for contraception or as hormone replacement therapy in post-menopausal women. Women who never conceive experience increase in exposure to oestrogen due to anovulation and are at risk.

Hereditary
Having a family member with uterine cancer increases the personal risk of developing the disease.


Obesity
Obesity increases the risk of uterine cancer.


Use of Tamoxifen
Long term use of Tamoxifen , a tablet used in Breast Cancer treatment, is a risk factor for Uterine cancer, especially in post menopausal women


Menstrual Related
Early onset of periods and late menopause increase risk.


Hereditary Uterine Cancer
A number of women carry high-risk disease-causing mutations for uterine cancer, that can lead to its occurrence at a younger age then usual. Such women maybe in their 30s and 40s. Deficiencies in the DNA mismatch repair genes result in the Lynch Syndrome in which there is a 70% risk of uterine cancer occurrence in the affected woman. Another rare disease is the Cowden Syndrome, where a mutation in the tumour suppressor gene predisposes to uterine cancer.


BRCA-Associated risk
BRCA mutation carriers may be predisposed to an increase in risk for Uterine cancers.


Breast-Uterine Cancer Risk
A personal history of Breast cancer increases the risk of uterine cancer occurrence.

Radiation-Induced risk
A prior history of pelvic radiation for treatment of another cancer increases the future risk of uterine cancer development.
Diagnosis of Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer diagnosis is usually suspected when there is abnormal bleeding in a premenopausal lady or postmenopausal bleeding or spotting.
However, it remains asymptomatic in the initial stages and may be detected incidentally when a thickened endometrial lining is seen on a routine ultrasound.
At times, it may be diagnosed on histopathology of a surgical specimen, when a hysterectomy is performed for another reason, like a fibroid, or excessive bleeding.

Ultrasound :
- It is generally the initial test performed. A thickened endometrial lining arouses suspicion. An endometrial biopsy is then taken for diagnosis by performing a dilatation & curettage (D&C), through a hysteroscopy via the vaginal route.
- The scopy allows a targeted endometrial biopsy to be taken.
- The pathology analysis then confirms the diagnosis.
- Once the uterine/endometrial cancer diagnosis is confirmed, a full-body PET-CT scan must be performed as a metastatic workup to assess the extent of the disease. This determines the next course of treatment.
- Routine lab studies, like CBC, and liver & renal function tests, must be done. Anaemia may be seen in women with heavy bleeding.
Non-Invasive Treatment Options for Uterine Cancer include
Which uses drugs to block the production or action of estrogen or progesterone.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells.
Cryoablation, which uses extreme cold to freeze and destroy cancer cells.
Frequently Asked Questions
Uterine cancer is staged using the FIGO system based on clinical and pathological information. It ranges from stage I (confined to uterus) to IV (spread to distant organs). Diagnostic tools include pelvic exams, imaging, and biopsies.
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that occur due to hormonal stimulation, they can be kept under observation or they can be treated surgically. Uterine cancer, on the other hand, is malignant and requires treatment with surgery, chemotherapy and radiation based on the stage of the disease.
Yes, uterine cancer can recur after treatment. Risk depends on stage, grade, and type of treatment received. Regular screenings are important to monitor for recurrence.
Hormonal imbalances, such as prolonged exposure to estrogen, can lead to the development of uterine cancer by stimulating the growth of the endometrial tissue which can lead to endometrial hyperplasia and eventually cancer.
Uterine cancer has no symptoms in early stages. Abnormal bleeding, abdominal pain, weight loss, weakness, anemia can occur later as cancer progresses.
Treatment for stage 1 uterine cancer depends on grade and histopathology. A radical hysterectomy which involves removal of uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes and lymph node dissection, radiation or brachytherapy, and chemotherapy may be used.
Stage 1 uterine cancer survival rate is extremely good, ranging from 80 to 100%.
Abnormal bleeding in premenopausal and postmenopausal women, including spotting and bleeding, can be a warning sign of possible uterine cancer.
Survival depends on the type of uterine cancer and the stage of the disease, untreated cancer will eventually prove fatal, it is difficult to give a definite time frame.


About Dr. Sujata Vasani
Dr. Sujata Vasani is a Hemato-Oncologist with 18+ years of experience in her field. She currently has her own clinic at Kemps Corner and is an Honorary Consultant at these renowned hospitals – Saifee, Breach Candy, Bhatia, Cumballa, and Dalvi.
Book An Appointment
Testimonials
Patient Case Studies
Case studies provide valuable insights into the treatment and management of individual cancer patients, informing oncologists’ decision-making and helping to improve care and outcomes for all patients. They also inform clinical guidelines and best practices, benefiting all cancer patients
Consultations with Uterine Cancer Specialists is just a call away!
Take the first step towards better treatment by reaching out to the expert team at the Uterine Cancer clinic in Mumbai. Schedule a consultation today!


